Framework description
In short, SOC is an international standard for the collection and exchange of information applicable to threat management systems for companies providing services (e.g. IT, payroll, accounting) for their clients. They apply to companies and organizations that process any sensitive data of their clients. They usually concern services such as:
- Cloud Computing
- Safety management
- Financial and accounting services
- Customer service centers
- Sales automation
- Processing of claims for medical services
A detailed description of the standard can be found here: see more.
The functioning international auditing standards are often confused, which probably results from their many similarities. The differences are discussed in detail with the client before the audit, we advise which standards to apply. Generally, an audit can be carried out according to the following standards:
- AICPA Audit according to SSAE 18 standard, and
- IFAC according to ISAE 3402 standard or according to ISAE 3000 standard
SOC. Types
SOC 1 - refers to the control mechanisms of the service provider that affect the financial statements of the service recipient. Therefore, it usually focuses on the specific needs of service recipients or auditors examining their financial statements and they are the primary users of the reports.
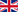
SOC 2 - the most commonly used report. Applies to non-financial processes (not focused on the impact on the financial statements) that are key to the quality of the service provided. The audit report is only available to existing clients (clients), as it contains a number of detailed information. Information on the successful audit opinion may be publicly available, which guarantees the quality of service to potential customers. Defines data management criteria in the context of five key areas (Trust Service Criteria):
- security - physical and logical security,
- availability
- processing integrity - integrity of processed data,
- confidentiality - confidentiality of information
- privacy - privacy of information
Both SOC 1 and SOC 2 audits can be conducted in Type I or Type II:
- Type I refers to the adequacy of the designed control mechanisms in these areas
- Type II refers to the adequacy and effectiveness of designed control mechanisms in these areas
| |
SOC 1
SOC 2
|
|
Certified period |
|
Subject |
|
| |
Type I |
|
On a specific audit completion date
|
|
Adequacy of designed controls
Describes the system and assesses its adequacy in the context of the standard's checkpoints
|
|
| |
Type II |
|
A minimum of 6 months, usually 1 year before the end of the audit
|
|
Adequacy and effectiveness of implemented controls
- Describes the system and assesses its adequacy in the context of standard checkpoints,
- Assesses whether the system actually works by testing during a certified period
|
|
SOC 3 - concerns key areas (Trust Service Criteria): security - physical and logical security, availability - availability, processing integrity - integrity of processed data, confidentiality - confidentiality, privacy - privacy. The audit report is also available to potential customers (may be publicly available) because it contains a limited range of data for the report according to SOC 2.
| |
Kategoria |
|
What? |
|
For whom? |
|
Access |
|
Why? |
|
| |
SOC 1 |
|
Controls over financial reporting |
|
Recipient of the service (accounting services) and recipient's auditor
|
|
Specific recipient of the service |
|
Preparation and audit of the financial statements |
|
| |
SOC 2 |
|
Physical and logical security, availability, integrity of processed data, confidentiality, privacy |
|
Board and management of the service provider
Specific customers - recipients of the service
|
|
Specific customers - recipients of the service |
|
Governance, Control and Risk certification,
Assurance for the service recipient
|
|
| |
SOC 3 |
|
Limited data range, but easy to read instead |
|
Any entity interested in assessing the service provider's control system |
|
Free access |
|
Marketing |
|
Prior to audit
The goal of our cooperation before signing the contract is to specify the scope of the audit and the type of SOC report.
1. Determining the scope of the audit is based on the exchange of information. Basically, it's important for us to get the answers to the following questions:
a) What service is to apply to SOC? - please provide a brief description of the service
b) What is the degree of description / ordering of the process? - we ask for information such as: are the objectives, risks and control mechanisms defined. Is any management system (e.g. ISO) implemented, or were there any audits in the area to be addressed by SOC?
c) What systems (IT and management systems) are used to provide this service?
d) Are the services provided from one or many locations?
e) For how many customers is the service provided? is the service progress the same for different customers?
2. Set the SOC report type. The main question is: SOC type I or SOC type II? To make a rational decision, please read the information in the "SOC. Categories" tab
SOC Audit
The goal of our clients is to obtain confirmation of compliance with the SOC requirements. Objective and independent assessment of the actual state is our duty.
To help our clients achieve the goal and conduct the audit in accordance with the standards, we have developed a proprietary audit approach, which consists of 3 steps:
1. Gap identification
Most of our clients do not have experience in meeting the requirements of the SOC standard. Therefore, conducting an audit without preparation is associated with a high risk of issuing a negative opinion, i.e. evidence of non-compliance. At the same time, however, the vast majority of deficiencies consist in the lack of formalization / description of the processes actually taking place.
That is why we usually start our work by making the client aware of the SOC requirements and indicating the "SOC gap", i.e. indicating what we think is missing to meet the SOC requirements. The SOC vulnerability is presented in our report from this stage of work. Of course, in the absence of a gap, we go straight to step 3.
The basic requirement is for the client to prepare a "system description", i.e. to define the objectives of the control system, risk and control mechanisms to manage them. We realize that "such a world view" does not have to be the everyday life of the customer. For us it is - we are able to help in the description of the system. During this stage, a system description and a declaration regarding its correctness are prepared - they will be certified by an auditor.
2. Bridging the SOC gap
In order to be able to obtain an independent and objective assurance of meeting the requirements, it is necessary to introduce solutions to eliminate the SOC gap. Our recommendations from the previous stage are the basis, the deadline for implementation is set individually.
3. Audit of compliance with the SOC requirements
When we receive information from the client that in his opinion the gap has been bridged and is ready to take the audit we agree on the appropriate audit date. Earlier, in order not to expose the client to costs, we make sure that the actions taken by the client give reasonable assurance that the gap has been closed. Depending on the maturity of the solutions adopted and the certainty of correct operation, the control systems are agreed with the client to conduct an audit:
• SOC 2. Type I. If there is no certainty that the actual operation of the control system will meet the requirements of SOC, we perform a type I audit first. This allows changes to be made to the concept of the control system before testing the actual control process - thus the customer again avoids unnecessary costs . After the implementation of the Type I audit and implementation of changes, it is possible to carry out the Type II audit.
• SOC 2. Type II. If both the customer and us are convinced that the actual course of the audit is correct we carry out a Type II audit. We run appropriate auditing tests based on our professional judgment, i.e. understanding of the client's system goals, risks associated with these goals and the vulnerability of individual areas to the risk and effectiveness of individual controls.
At the end of our work, we present an opinion on the degree of compliance with the SOC standard and a report on the audit carried out with detailed reference to individual requirements of the standard. The opinion is an independent and objective statement of compliance with the SOC requirements.
Competences
SOC audits are carried out by experienced auditors with relevant knowledge and international certificates. The audit may be conducted in Polish or English.
The audit process is supervised by an auditor with CPA privileges granted by AICPA. Audit opinion and report are certified by a CPA auditor.
The team's competences are confirmed by international certificates: CPA, CISA, LA ISO 27001, CCSA, CIA, CGAP, CRMA, COBIT2019F.